Release 10th December 2025
Change Control note Hiperspace --version 2.5.21 HiLang --version 2.5.21
Overview
This release introduces GPU optimization for graph searches involving HiperEdge and other vector operations used in nearest-neighbor searches (commonly required when providing information for AI prompts).
It also enhances Hiperspace functions for LINQ queries by adding automatic null-coalescing for values selected from Hiperspace, supporting non-sargable join conditions, and improving performance for multi-table joins and HiperspaceDB cube aggregation.
CalculationGPU
Graph Theory is a branch of Mathematics that can be used to describe all knowledge as Node and Edge's between them; because there is a simple consistent model across domains it has wide application for visualizing information, but has the downside that many graph views appear as a tangled web of nodes and lines: often conveying complexity, but not clarity.
HyperGraph is a generalization of Graph that replaces the tangle of edges with a hyperedge that encapsulates all the intermediate nodes that are not interesting: I have a cousin (Robert), which can be described as "Me->(cousin)->Robert", but cousin is actually a hyperedge that is derived from "me->mother2->mother1->daughter->son where mother2 is not daughter"
HiperEdge is a HiperSpace implementation of hyperedge that encapsulates the source of the hyperedge for a simple view of connections or the intermediate nodes in the path. When viewed graphically a HiperEdge view looks like a tree of connections extending out from the subject Node.
Hiperspace provides functions to query HiperEdges using rules that project {source node type, edge type, end node type} to create HiperEdges whenever needed (e.g. as a member function of a Node).
Graph support
This version introduces ICalculationGPU for optional acceleration of Graph Queries using the hardware created for Ray Tracing,
Calculation support
Search for Nearest node proximity in a Vector Space is supported via GPU, together with aggregation of Vectors used for complex calculation.
Null Coalesce
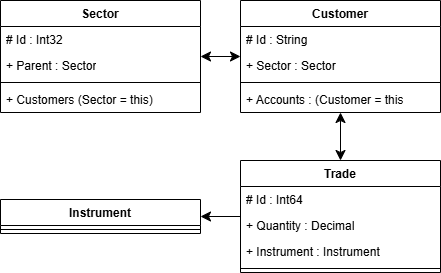
Consider a cube analytics model with {Sector, Customer, Account, Trade} with dimensions Customer and Sector; with Trade Facts aggregated. Null-coalescing is necessary when querying dimensions associated with a Trade fact.
@CubeDimension, CubeHierarchy(Parent), Versioned
entity Sector
(Id : Int32)
{Name : String, Parent : Sector}
[Children : Sector (Parent = this), Customers : Customer (Sector = this)];
@CubeDimension, DeltaIndex
entity Customer
(Id : String)
{Sector : Sector}
[Name : String, Accounts : Account (Customer = this)];
entity Instrument;
entity Account
(Id : String)
{Name : String, Customer : Customer};
@CubeFact, DeltaIndex
entity Trade : Versioned
(id : Int64)
{@CubeMeasure(Aggregation.Sum) Quantity : Decimal, Instrument : Instrument, Account : Account};
The query from trade in Space.Trades select trade.Account.Customer.Sector provides the Sector for a trade, but if any {Trade.Account, Account.Customer, Customer.Sector} is missing the expression will break. The work around is to manually add null-coalesce to the query:
from trade in Space.Trades
select trade.Account == null ? null :
trade.Account.Customer == null ? null :
trade.Account.Customer.Sector;
This release adds coalesce automatically. This is especially useful when Hiperspace.SQL is used to query a hiperspace from a scripting language where null-coalesce is not available, but we want to access the graph of properties.
select c.Id as SectorId, a.Id as AccountId
from Account as a join
Customer as c on a.Customer.Id = c.Id
group by c.Sector.Id, a.Id;
This query would have previously failed if a.Customer is missing.
Non-Saragable predicates
In Hiperspace the following query cannot be Sargable since Customer does not contain a Sector but a KeyRef<Sector.KeyType, Sector> with lazy loading of the element if needed.
select Sector.Name as "Sector Name", c.Name as "Customer Name"
from Sector join
Customer on Sector.Name = Customer.Sector.Name
order by Sector.Name, Customer.Name;
This query would previously have failed since Customer.Sector is a derived property of Customer and cannot be applied to a template for a Find() request of matching Customers
This release splits join processing into Sargable predicates and residual conditions and is constructed dynamically as compiled expressions.
Release 30th January 2026 Release 17th January 2026 Release 31st December 2025