Enterprise Lineage | Implementing Pathwise Complexity | Data Input Validation
Pathwise Complexity is technique to measure the complexity of a BPMN process with emphasis on of decisions and particularly the consequences of re-work/re-check. All well-formed business processes begin with one or more start-events, and proceed through a sequence of activities decisions, gateways and intermediate events until they end at one or more end-events: Business processes are closed graphs that have finite number of paths from start to finish.
Pathwise Complexity assists process improvement by ranking processes that are most receptive to improvement. Process improvement techniques like Six-Sigma are iterative – if you fix the worst processes, eventually they will all be good.
Pathwise complexity is inspired by the Cyclomatic complexity in software engineering that uses the total number of nodes and total number connections between them to compute a score, but with the distinctions:
- Cyclomatic complexity explicitly ignores the algorithmic complexity of iterating over a list rather than treating each item in a list as a distinct activity. In software engineering exceptions can be raised at a number points that can not be mapped to an orderly flowchart from start to finish.
- Activities in software have low cost relative to activities in a business process and business decisions are more expensive than activities.
- Rework in a business process is exponentially more expensive than preparatory activities and non-looping decision. Pathwise Complexity makes axiomatic assumptions:
- A path that does not reach an end is not complex, it does not work. Complexity score is not a substitute for quality – quality assurance metrics also need to be captured.
- Actors are intelligent enough not to keep making the same decision over and over again unless some decision has changed.
Pathwise complexity is calculated by:
- Mapping ever distinct path from start to finish branching to different paths following decisions and gateways
- If an activity is reached that was previously visited in the path, check it was visited by a different route from last time.
[1]->[2]->[3]->[2]is ok because[1]->[2]and[3]->[2]are different routes, but[1]->[2]->[3]-[2]->[3]is not because the route[2]->[3]is cyclic and therefore invalid. - Count the total number of distinct paths
- Calculate the standard deviation of distinct paths across all processes, and use the bands to classify them into {High, Normal, Low)
There is a high correlation between the Pathwise Complex Process and Processes that can be improved. Automatic calculation is critical to it being a viable approach
Examples
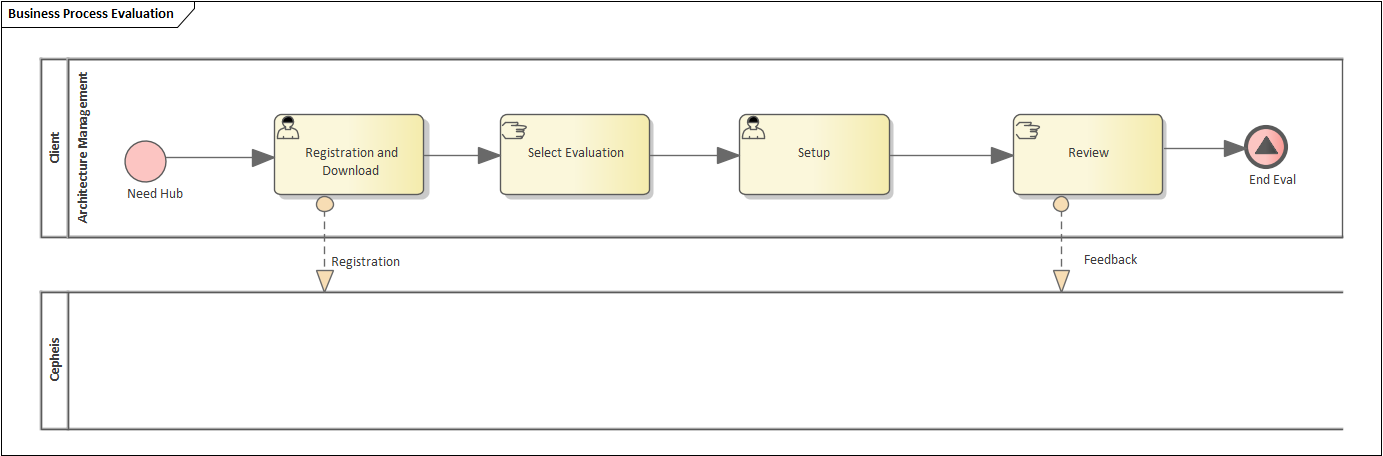
The Evaluation process has low Pathwise complexity because there is one path
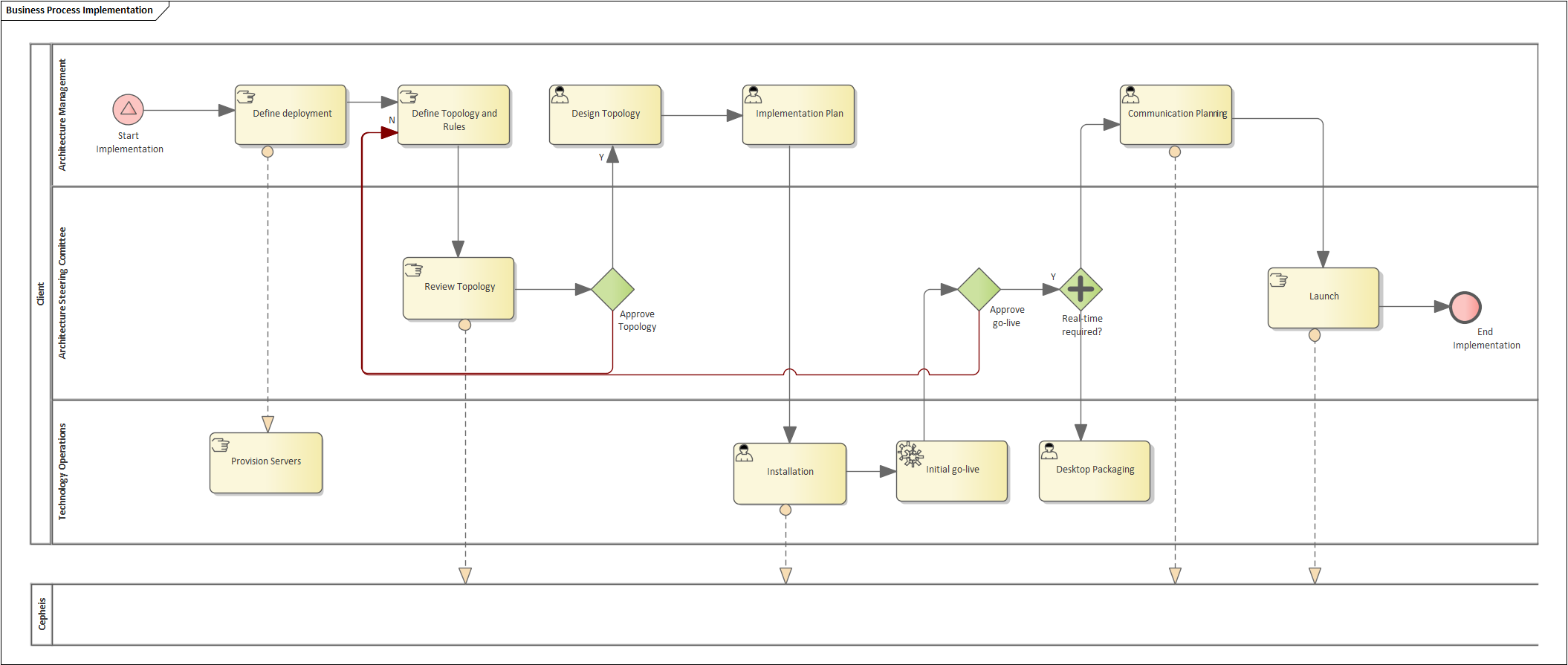
The Implement Process has Normal Pathwise Complexity because there are five distinct paths
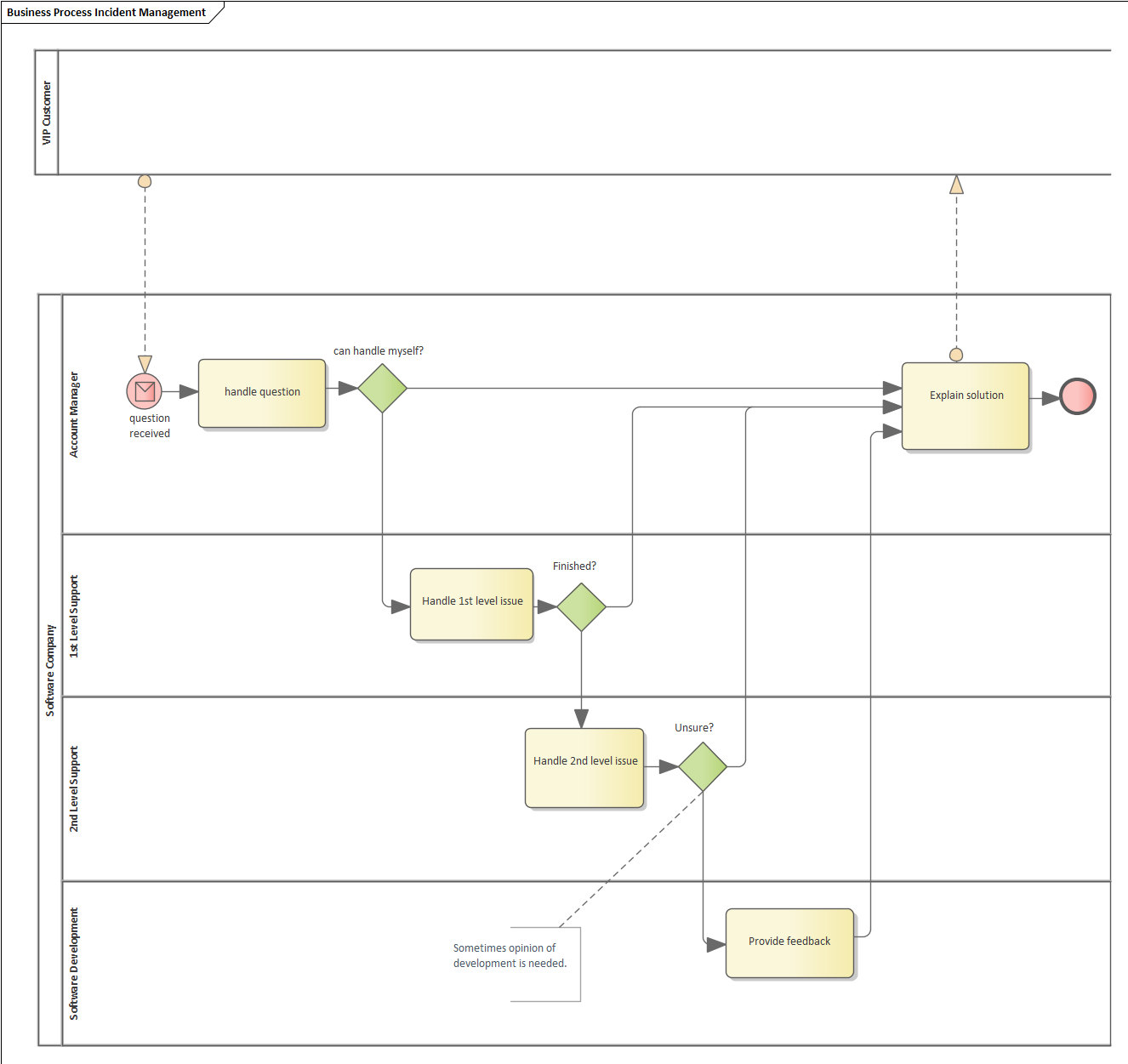
 The Process Incident Management has High Pathwise Complexity because there are 128 paths (due to the feedback loop to VIP Customer, who might raise additional questions from the answer).
The solution to the high pathwise complexity is not to model 'VIP Customer' as a black-box, but instead as a dialog where the customer is expected to review the answer before closure.
The Process Incident Management has High Pathwise Complexity because there are 128 paths (due to the feedback loop to VIP Customer, who might raise additional questions from the answer).
The solution to the high pathwise complexity is not to model 'VIP Customer' as a black-box, but instead as a dialog where the customer is expected to review the answer before closure.
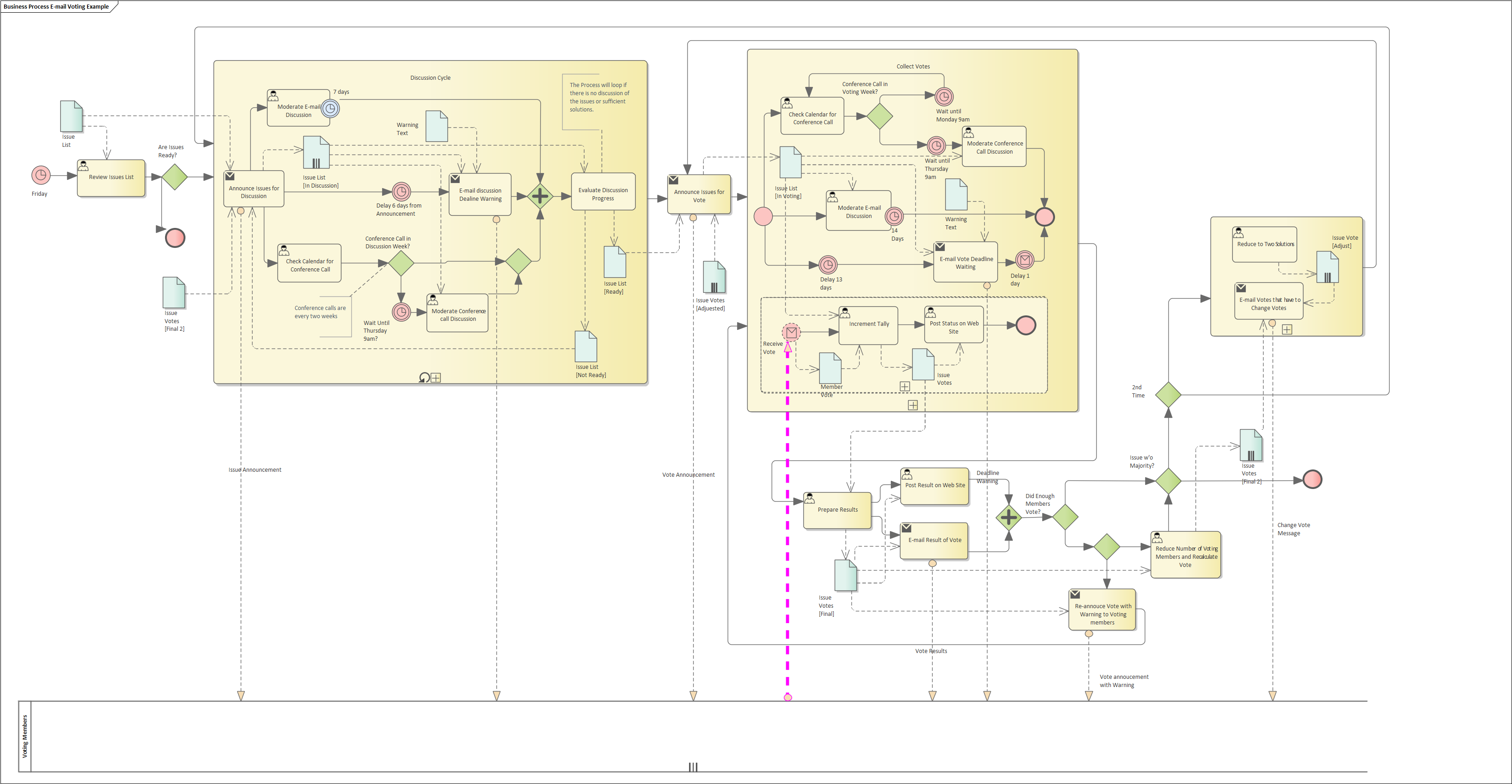
 The limit to the methodology is that Black-box lane often embed hidden assumptions about time ordering of behavior that results in the "E-main voting example" reporting a Pathwise complexity of 7,164,676
because "Receive Vote" (in pink) can be sent at any time. Either black boxes are a defective design pattern, or messages need to be excluded from complexity analysis
The limit to the methodology is that Black-box lane often embed hidden assumptions about time ordering of behavior that results in the "E-main voting example" reporting a Pathwise complexity of 7,164,676
because "Receive Vote" (in pink) can be sent at any time. Either black boxes are a defective design pattern, or messages need to be excluded from complexity analysis