Release 14th April 2025
Change Control note --version 2.2.1
Overview
This release extends the Hipperspace model to better support streaming aggregation of Cube and viewing of aggregates part of graph view. It also updated SessionSpace to use stream replication rather than Zip file compression.
Cube aggregation
Traditional OLAP Cubes do not include the notion of history unless includes as a dimension in the cube, and are either calculated
- Multidimensional cubes recalculated each night
- Relational cubes are translated into the SQL queries that aggregate at a point in time from source data
- Hybrid cubes combine an overnight batch with intraday relational updates
Hiperspace includes history for element stored in Hiperspace with access to the full history of the element. Cube data is not overwritten whenever a value is changed intraday, but a new version is created. This allows a point-in-time view of a SubSpace to be opened, or history to be used for regression analysis over time (A portfolio/book view can be aggregated in a cube and trend-line examined as the data changes). Traditionally the value of the latest summary (e.g. total-sales per product) is discounted by the frequency it is examined (you wouldn't want to calculate a per-minute summary for a product if you only analyze it once a day) and the cost of recalculating it each night if only reviewed at month end.
When you add the capability for regression analysis, the value of each observation increases: we presume that historical values will be re-used many times, and calculate the projection for fast access to data.
Stream aggregation
Hiperspace uses Delta indexes to fast access to changes within a short epoch, and version history to calculate the delta from the last epoch. The a price change to APPL.N stock will only update the portfolio that reference this stock, and not require the reaggregation of the entire portfolio (if APPL.N changes from $300 to $290 for a portfolio of 100 shares, the value of the portfolio changes by $-900, which is added to the current portfolio value) . Point-in-time AsAt views of the SubSpace are used to perform aggregation concurrently with other changes (which will be included in the next epoch calculation) without degradation to performance.
code changes
Additional interfaces are added for runtime access to Cube data:
- CubeDimension property of a {
entity,segment,aspect} now includes anICubeDimensioninterface that includes the CubeSlice string (used to directly access the summary value for a cube node, without retriveing intersection with other dimensions - CubeHierarchy property to indicate that the dimension is part of a hierarchy and aggregates for levels in the hierarchy should be calculated in addition to the leaf values
- CubeFact property of of a {
entity,segment,aspect} now includesICubeFactfor the fact table, and includes methods to add dimensions and retrieve values generically.
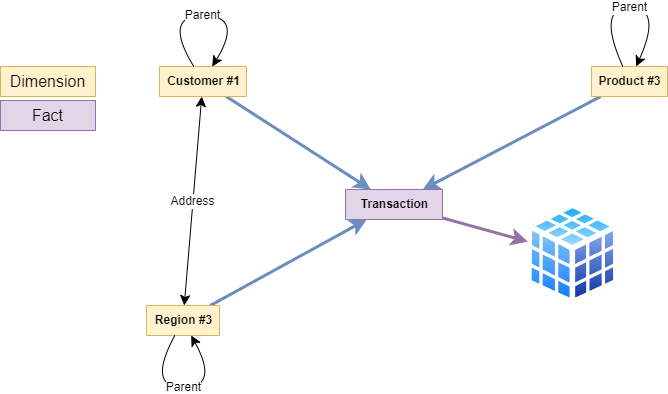
These methods enable cube data to be viewed as part of graph view. When a Cube Dimension is a graph node, a Node view is added fact table with two edges Dimension-(Fact)->Fact for traversal from dimennsion to fact, and Fact-(Dimension)->Dimension for traversal from Fact to the Dimension.
For example, a Cube of Transactions with dimensions {Customer, Product, Region}, the addition of Fact Nodes creates transitive edges for {Customer->Product, Customer->Region, Product->Region} via transaction fact. When combined with Transitive Edges (Hyper Edges) it becomes possible to view to Cube data through a graph view in a Hypergraph.
For the Customer "British Steel" (Client Node), and "Coking Coal" (Product Node) the Quantity Fact contains the total available ( "British Steel" -> "Coking Coal" -> Quantity Edge), and ( "British Steel" -> "Coking Coal" -> "Scunthorpe" -> Quantity Edge) references only the total currently in that region.
Transitative Edge becomes Hiper Edge
The name of SetSpace TransitiveEdge has been changed to HiperEdge better distinguish Graph Edges that are transitively projected as Hiper-edges, from edges that might themselves be transitive without being projected. This breaking change is used because Hiper-Edges can be viewed as Cube edges where each step in a Cube Edge is also a drill-down into the dimensions of a Cube for the dimensions in the hipergraph.
HiperEdge is used instead of the mathematically correct hyper-edge (within a Hyper-Graph because our implementation explicitly includes the references to the Hiper Edge (extended) and Edge (projected): The inclusion of the path enables the identification of each Dimension and CubeSlice referenced
Hiperspace.DB
Hiperspace.DB provides functionality to project Edge to HiperEdge, and aggregate Fact Cubes close to the data without network access - especially important for web-assembly clients that may be accessing the Hiperspace over the internet.
Edges, HiperEdges and Facts can be used in SQL queries (our implementation of SQL allows joins to nested sets (syntax appears as a cross-join since the actual join is created by ownership).
select p.Name as Person,
r.To.Name as Relation,
r.TypeName as Relationship,
r.Length as Length,
r.Width as Width
from Persons as p,
p.AllRelatives as r
where p.Name = :name;
SessionSpace
HiperSpace has additional streaming methods for ExportAsync and ImportAsync for bulk data import, but also for SessionSpace which might exceed message sizes when saving a large amount of data over the internet. The legacy Space() function has is now [Obsolete], and will be removed in a future release
Hilang
The Hilang AOT compiler has been updated to provide the implementation for the ICubeDimension and 'ICubeFact` views.